Digital currency is reshaping how businesses handle money, but the hype doesn’t tell the whole story. Smart companies need to understand both the opportunities and the pitfalls before jumping in.
We at Web3 Enabler see businesses wrestling with digital currency advantages and disadvantages daily. The reality? It’s not as simple as the headlines suggest.
What Digital Currency Actually Means for Businesses
Digital currency represents electronic value that exists without physical form, but business applications extend far beyond Bitcoin headlines. Virtual currencies remove geographical payment barriers and enable transactions that are faster and more accessible than traditional banks offer. The Internal Revenue Service classifies virtual currencies as digital values for tax purposes, which creates compliance obligations for any business that handles cryptocurrency trades. Companies must understand that digital currency encompasses everything from Bitcoin and Ethereum to closed systems like airline miles that function only within designated platforms.
Three Categories That Matter for Operations
Open virtual currencies like Bitcoin convert to both fiat money and other cryptocurrencies, which creates tax implications and accounting complexities. Closed virtual currencies operate within specific ecosystems and cannot convert to real money, which limits their business utility. Central Bank Digital Currencies represent government-backed digital versions of national currencies, with 114 countries exploring CBDCs and China’s digital yuan already serves 180 million personal wallets.
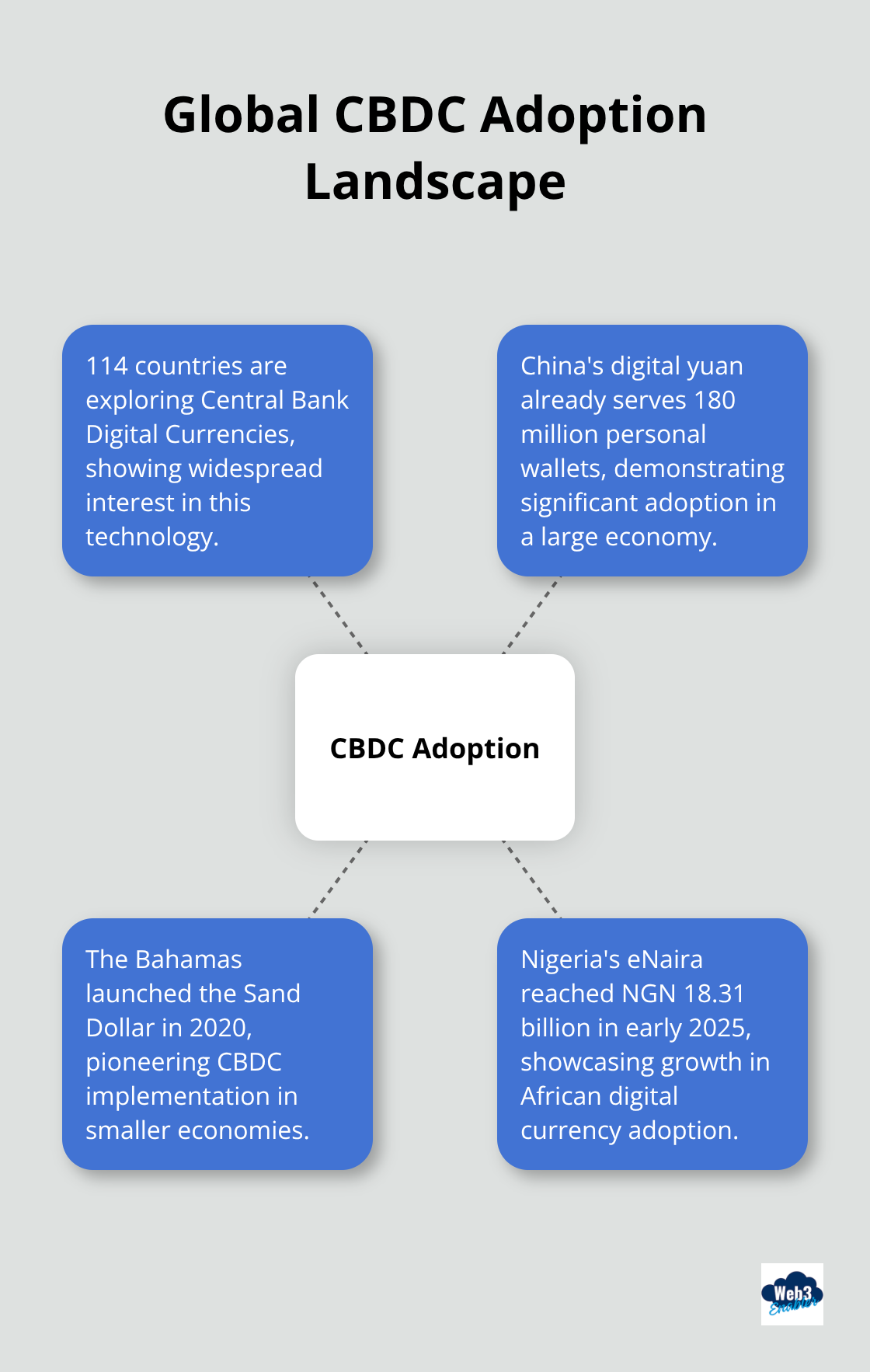
The Bahamas launched the Sand Dollar in 2020 with $1.4 million in circulation, while Nigeria’s eNaira reached NGN 18.31 billion in early 2025. These systems integrate with current financial infrastructure through APIs and middleware, which allows businesses to adopt digital payments without complete overhauls of current processes.
Payment Processing Revolution
Digital currencies eliminate intermediaries in financial transactions and connect buyers and sellers directly while they reduce processing costs. A medium-sized business could save approximately $114,000 annually on transaction fees with CBDCs (assuming a 0.1% processing fee compared to traditional payment systems). Cross-border payments benefit most dramatically, with the Bank of England demonstrating that blockchain technology reduces international payment costs up to 70%.
Traditional systems like Visa process up to 65,000 transactions per second, while Bitcoin manages only 7 transactions per second. This highlights infrastructure limitations that businesses must consider before they make the switch.
Integration Challenges With Banking Systems
Digital currencies coexist with traditional banks rather than replace them entirely. CBDCs provide additional payment options while they maintain cash accessibility and privacy features. Project mBridge, initiated through the United Arab Emirates, facilitates faster cross-border transactions between nations that participate with digital currencies.
Banks face potential deposit losses if consumers prefer digital wallets, which pushes financial institutions to innovate service delivery and user experience. Regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, with the European Central Bank that tests designs for a digital euro expected to conclude in late 2025.
Risk Factors That Demand Attention
Price volatility creates significant investment risks, with cryptocurrency values that experience substantial swings and impact business cash flow. Security threats target virtual currencies frequently and pose risks to business operations and customer data. Unregulated virtual currencies lack legal protections for users, which requires careful storage and spending protocols.
Technical challenges include internet access requirements that may limit adoption in rural business locations. These infrastructure realities shape how companies can actually implement digital currency solutions, which leads us to examine the specific advantages that make businesses consider this technology despite the challenges.
Digital Currency Advantages for Modern Businesses
Digital currency transforms business operations through measurable cost reductions and speed improvements that traditional payment systems cannot match. The Bank of England documented 70% reductions in cross-border payment costs when businesses implement blockchain-based systems, while JPMorgan’s blockchain loan platform cut approval times by 30% through automated processes. Companies that process international transactions save $9,500 monthly on average when they eliminate intermediary banks that charge multiple fees for currency conversion and wire transfers.
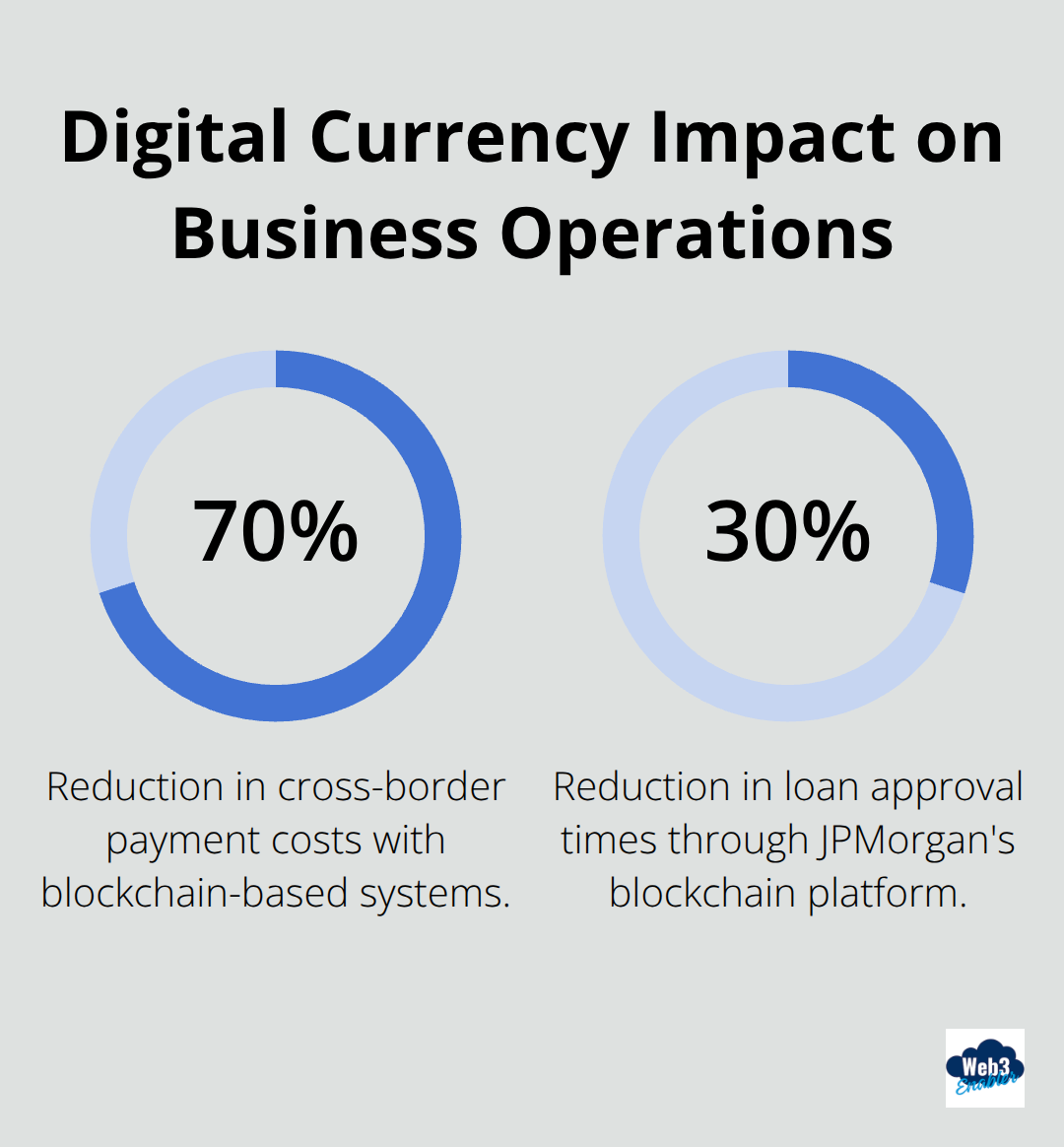
Speed That Actually Matters for Cash Flow
Traditional wire transfers take 3-5 business days for international payments, but digital currencies complete cross-border transactions within minutes regardless of bank hours or holidays. Walmart and IBM demonstrated instant food recall capabilities through blockchain traceability and reduced response times from weeks to seconds when contamination issues arise. APAC region businesses experienced 69% growth in on-chain crypto activity from $1.4 trillion to $2.36 trillion, which shows real adoption beyond speculation. Latin America followed with 63% growth as businesses discovered digital currencies solve remittance challenges and bank access limitations.
Security Through Mathematical Proof
Blockchain technology creates permanent audit trails that simplify compliance reports and reduce fraud by 40% according to Aetna and Anthem insurance implementations. Each transaction gets verified by thousands of network nodes rather than single points of failure that hackers target in centralized systems. Estonia pioneered digital identity solutions through blockchain for e-governance and proved government-level security applications work at scale. Smart contracts eliminate human error in repetitive transactions while they provide transparency that builds trust between business partners who previously required expensive legal intermediaries.
Global Market Access Without Bank Barriers
Digital currencies reach the half of adults around the world who remain unbanked, which expands potential customer bases dramatically. Sub-Saharan Africa showed 52% growth in crypto adoption as businesses use digital currencies for everyday transactions when traditional bank infrastructure fails. Stablecoins like USDT processed over $1 trillion monthly while USDC handled $1.24-3.29 trillion, which demonstrates business confidence in digital payment stability over volatile cryptocurrencies.
These advantages paint a compelling picture, but smart businesses know every innovation comes with trade-offs. The same technology that offers these benefits also introduces new risks that require careful consideration.
Digital Currency Risks and Challenges
Digital currency volatility destroys cash flow predictability faster than any CFO wants to experience. Bitcoin lost 65% of its value between November 2021 and June 2022, which means a company that held $100,000 in Bitcoin would face $65,000 in losses within seven months. Ethereum dropped 78% during the same period, while smaller cryptocurrencies experienced even more dramatic swings.

Businesses that accept cryptocurrency payments without immediate conversion to fiat face constant exposure to these price movements. Afghanistan demonstrated extreme adoption volatility after the US withdrawal in 2021, which shows how political events can eliminate crypto activity overnight in entire regions.
Regulatory Maze Without Clear Exit Signs
The European Union’s Markets in Crypto Assets regulation defines crypto-assets broadly and creates compliance burdens that small businesses struggle to manage. Companies that operate across borders face different requirements as countries develop different CBDC frameworks simultaneously.
The Internal Revenue Service treats virtual currency trades as taxable events, which means every cryptocurrency transaction creates accounting obligations and potential audit triggers. Crypto KYC requirements add additional compliance layers that businesses must navigate. Nigeria’s eNaira represents a small fraction of cash circulation despite government backing, which shows regulatory support alone cannot guarantee adoption success.
Eastern European countries like Ukraine and Moldova show high adoption rates when adjusted for population, but this correlation with economic instability demonstrates that regulatory uncertainty drives cryptocurrency use rather than business confidence.
Security Threats That Cost More Than Money
Hackers target virtual currencies more aggressively than traditional payment systems because blockchain transactions cannot be reversed once confirmed. The decentralized nature that provides security benefits also eliminates customer service departments that can freeze accounts or reverse fraudulent charges.
Illicit transactions represent a small percentage of all cryptocurrency activity according to industry analysis, but this still translates to significant fraud losses in absolute terms. Technical infrastructure requirements create additional vulnerability points, as internet outages or cyber attacks can prevent businesses from accessing digital funds when they need them most.
Infrastructure Dependencies That Fail When You Need Them
Rural businesses face particular challenges since reliable internet access remains inconsistent, which makes digital currency payments unreliable compared to cash or traditional card processing systems that work offline. Bitcoin processes only 7 transactions per second compared to Visa’s much higher transaction capacity, highlighting scalability limitations during peak usage periods.
Network congestion can delay transactions for hours or days while transaction fees spike during high-demand periods, which creates unpredictable costs for businesses that rely on timely payments.
Final Thoughts
Digital currency advantages and disadvantages create a complex decision matrix that demands honest assessment rather than hype-driven choices. The 70% cost reductions in cross-border payments and $114,000 annual savings on transaction fees represent real opportunities, but volatility risks that eliminated 65% of Bitcoin’s value in seven months cannot be ignored. Smart businesses focus on specific use cases rather than broad adoption strategies.
Companies that process significant international transactions benefit most from digital currency implementation, while businesses with stable domestic operations may find traditional systems adequate. Regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, with 114 countries that explore CBDCs and the European Central Bank that concludes digital euro tests in late 2025. Infrastructure readiness determines success more than enthusiasm (rural businesses face internet dependency challenges, while urban companies must navigate compliance requirements that vary by jurisdiction).
The key lies in matching digital currency capabilities with actual business needs rather than following market trends. We at Web3 Enabler help businesses navigate this transition through Salesforce-native blockchain solutions that integrate with existing corporate infrastructure. Our approach focuses on practical applications like stablecoin payments and global transfers rather than speculative investments.






