Blockchain compliance has become the defining challenge for enterprises entering Web3 in 2025. Regulatory frameworks are evolving rapidly across jurisdictions, creating complex requirements for businesses.
Blockchain compliance has become the defining challenge for enterprises entering Web3 in 2025. Regulatory frameworks are evolving rapidly across jurisdictions, creating complex requirements for businesses.
We at Web3 Enabler see companies struggling to balance innovation with regulatory adherence. The stakes are higher than ever, with non-compliance risks including hefty fines and operational shutdowns.
Understanding Blockchain Compliance Requirements in 2025
The regulatory landscape for blockchain businesses has crystallized around three primary compliance pillars. The U.S. GENIUS Act, passed on July 18, 2025, established mandatory 100% reserve backing for stablecoins and created federal licensing pathways that enterprises must navigate. The EU’s Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) now governs the most comprehensive crypto framework globally, while the UK plans implementation by late 2026. These frameworks demand specific operational changes: companies must implement real-time transaction monitoring systems, maintain detailed audit trails, and establish clear governance structures for digital asset management.

Anti-Money Laundering Implementation Standards
AML requirements have intensified significantly in 2025, with transaction monitoring systems now analyzing over 270 risk indicators on blockchain transactions. Financial institutions must screen crypto wallet addresses against sanctions lists and monitor Politically Exposed Persons continuously beyond initial onboarding. The prevalence of AML gaps in the cryptocurrency sector, highlighted by enforcement cases like KuCoin, demonstrates that companies need automated ID verification that supports over 4,000 document types from 240+ countries. Compliance teams report operational cost savings when they implement automated workflows that include real-time PEP screening and adverse media monitoring.
Data Protection Framework for Blockchain Operations
Blockchain’s immutable nature creates unique challenges for data protection compliance under GDPR and similar regulations. Companies must architect privacy-preserving solutions that allow authorized access while they maintain transparency requirements. The rise of AI-driven identity fraud and deepfakes has made liveness checks and robust security protocols mandatory during customer verification processes. Organizations need multi-signature protocols and verifiable record systems that outperform traditional asset protection methods while they meet regulatory data retention and deletion requirements.
Cross-Border Regulatory Coordination
Asian jurisdictions showcase varied regulatory strategies, with Singapore overseeing local crypto firms and Hong Kong positioning itself as a digital asset hub. This fragmented approach creates operational complexity for global blockchain businesses that must comply with multiple frameworks simultaneously.

Companies face the challenge of adapting their compliance infrastructure to meet different jurisdictional requirements while they maintain operational efficiency across markets.
These regulatory foundations set the stage for the practical compliance challenges that blockchain businesses encounter daily in their operations.
Common Compliance Challenges for Blockchain Businesses
Blockchain businesses face three fundamental compliance conflicts that traditional regulatory frameworks cannot resolve effectively. The transparency versus privacy paradox creates the most significant operational challenge: while regulators demand complete transaction visibility for AML compliance, data protection laws require privacy controls that blockchain’s immutable nature cannot accommodate. Companies must implement privacy-preserving technologies like zero-knowledge proofs or layer-two solutions that add complexity and costs to their infrastructure. The Department of Justice’s dissolution of its National Cryptocurrency Enforcement Team signals a shift toward targeting willful violations, but businesses still struggle with automated compliance systems that can analyze risk indicators while they maintain user privacy.
Transaction Transparency vs Privacy Requirements
Regulators require complete visibility into blockchain transactions for AML monitoring, yet GDPR and similar privacy laws mandate data protection controls that conflict with blockchain’s transparent nature. Companies cannot simply delete transaction records to comply with “right to be forgotten” requests because blockchain’s immutability prevents data modification. This creates legal liability when customer data remains permanently visible on public ledgers. Privacy-preserving solutions like zero-knowledge proofs enhance privacy, security, and efficiency for businesses while adding technical complexity and operational costs. The conflict intensifies when companies operate across jurisdictions with different privacy standards (EU’s strict GDPR versus more flexible U.S. frameworks).
Smart Contract Legal Liability Gaps
Smart contracts operate without legal precedent for liability assignment when automated processes violate regulations or cause financial harm. Current legal frameworks require human decision-makers for regulatory accountability, but smart contracts execute automatically based on coded parameters. Companies face unclear liability exposure when these contracts interact with sanctioned addresses or process transactions that violate AML requirements. The lack of standardized audit procedures for smart contract compliance creates additional risk, as traditional legal review processes cannot adequately assess code-based financial operations. Enterprises need specialized legal expertise that combines blockchain technical knowledge with regulatory compliance understanding, but few law firms offer this hybrid capability at scale.
Cross-Border Regulatory Differences
Operating across multiple jurisdictions multiplies compliance costs exponentially rather than additively. Singapore’s oversight requirements differ fundamentally from Hong Kong’s digital asset hub approach, forcing companies to maintain separate compliance infrastructures for each market. The EU’s MiCA framework requires different operational procedures than the U.S. GENIUS Act’s federal licensing pathways, creating incompatible compliance systems that cannot share resources or data efficiently. Companies report increased compliance costs when they operate in multiple jurisdictions compared to single-market operations. The fragmented regulatory landscape prevents economies of scale in compliance operations, making international blockchain business expansion prohibitively expensive for smaller enterprises.
These operational challenges demand strategic solutions that address both technical implementation and regulatory adherence across multiple frameworks.
Best Practices for Blockchain Compliance Implementation
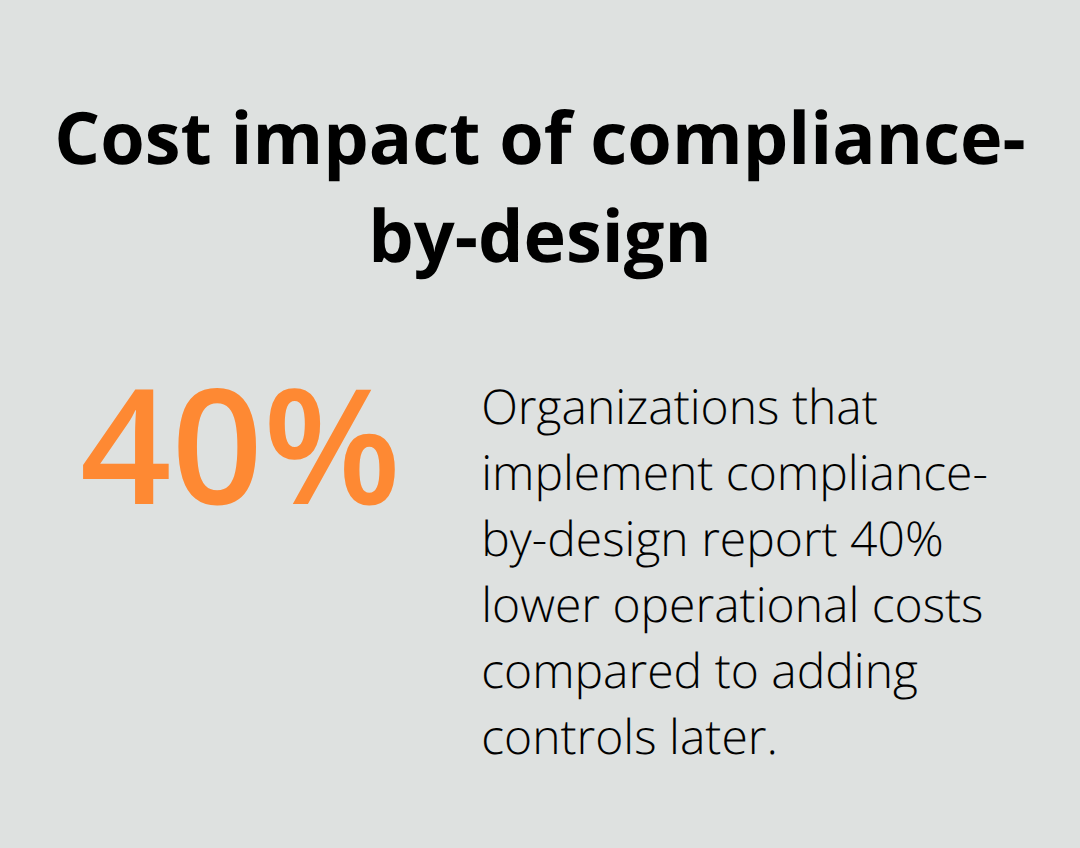
Companies must make three fundamental design decisions that determine long-term regulatory success when they architect blockchain systems. Organizations need to build privacy-preserving solutions from day one rather than add compliance controls after deployment. The most effective approach combines multi-signature protocols with automated compliance monitoring systems that analyze over 270 risk indicators in real-time. Organizations that implement compliance-by-design report 40% lower operational costs compared to companies that add compliance layers after launch. The architecture must support continuous monitoring for PEPs, sanctions screening, and adverse media detection while it maintains the decentralized benefits that make blockchain valuable for business operations.
Real-Time Transaction Monitoring Architecture
Automated compliance monitoring systems must integrate directly with blockchain nodes to capture transaction data in real-time rather than rely on periodic batch processing. The most successful implementations use API-driven architectures that connect compliance databases with blockchain transaction feeds, which enables immediate risk assessment when transactions occur. Companies need systems that support over 4,000 identification document types from 240+ countries for global operations, with automated reminders for document expiration dates to maintain ongoing compliance status. The key lies in selecting monitoring platforms that provide bank-grade security measures while they offer customizable multi-scope features for different subsidiaries within a single compliance framework.
Smart Contract Compliance Integration
Smart contracts require specialized audit procedures that traditional legal review processes cannot adequately assess. Legal expertise becomes critical when smart contracts interact with regulatory requirements because code-based financial operations execute automatically without human oversight. Companies must implement compliance checks directly into smart contract code rather than rely on external monitoring systems that cannot prevent non-compliant transactions. The most effective approach involves programmable compliance rules that automatically reject transactions involving sanctioned addresses or amounts that exceed AML thresholds.
Expert Partnership Selection Criteria
Companies need specialized legal and regulatory experts who combine blockchain technical knowledge with regulatory compliance understanding, though few law firms offer this hybrid capability at enterprise scale. The most effective partnerships involve compliance consultants who understand blockchain’s immutable nature conflicts with data protection requirements like GDPR’s right to be forgotten. Companies should prioritize experts who have experience with the U.S. GENIUS Act’s federal licensing pathways and the EU’s MiCA framework, as these represent the most comprehensive regulatory environments globally. The partnership must address smart contract liability gaps where automated processes might violate regulations without clear accountability structures that traditional legal frameworks require.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain compliance success demands proactive architectural decisions rather than reactive regulatory responses. Companies that integrate compliance systems which analyze 270+ risk indicators from launch achieve 40% lower operational costs than those who add controls later. The regulatory landscape will continue to consolidate around frameworks like the U.S. GENIUS Act and EU’s MiCA, which creates standardized requirements that reduce cross-border complexity.
Business leaders must prioritize three strategic actions: implement privacy-preserving solutions that satisfy both transparency and data protection requirements, establish partnerships with blockchain-specialized legal experts, and architect systems that support automated compliance workflows. The convergence of AI and blockchain compliance will accelerate, which makes real-time risk assessment standard practice. Organizations that adapt early will gain competitive advantages in the evolving regulatory environment.
Companies need platforms that connect blockchain transactions directly to existing corporate infrastructure. We at Web3 Enabler provide native Salesforce integration for digital assets, which enables businesses to manage crypto payments and track investment returns within familiar systems while they maintain regulatory compliance across global operations. The future belongs to organizations that treat blockchain compliance as a strategic advantage rather than a regulatory burden.





![Navigating Compliance in the Blockchain Era [2025]](https://web3enabler.com/wp-content/uploads/emplibot/blockchain-compliance-hero-1761160171.jpeg)