Digital currency vs cryptocurrency sounds like the same thing, right? Wrong. These two terms get tossed around like confetti at a fintech conference, but they’re actually quite different beasts.
We at Web3 Enabler see businesses mixing these up daily, and honestly, it’s causing some pretty expensive confusion. Time to set the record straight once and for all.
What Exactly Is Digital Currency
Digital currency is electronic money that central authorities like governments or financial institutions control. Think of it as the digital twin of your regular cash, but with a boss who watches every move. These currencies exist entirely in digital form and central systems manage them completely.
The key difference from physical money is speed and accessibility. Central Bank Digital Currencies like China’s digital yuan already serve over 260 million users, while the European Central Bank plans to launch its digital euro by 2026. Stablecoins represent another major category, with USDC in circulation at approximately 70 billion tokens backed by short-term government treasury bills.
Companies like Shopify and Stripe now integrate stablecoins into their payment systems because they cut transaction fees and boost processing speed dramatically. The Federal Reserve estimates that digital payments could reduce cross-border transfer costs by up to 80% compared to traditional banks.

Government-Controlled Digital Money
Central banks worldwide race to launch their own digital currencies. The Bahamas launched the Sand Dollar in 2020, while Nigeria’s eNaira reached 13 million wallet downloads by 2023. These currencies give governments unprecedented control over monetary policy and spending patterns (plus they can track every purchase you make).
Corporate Stablecoins Take Over
Private companies issue stablecoins pegged to traditional currencies. Circle’s USDC maintains its dollar peg through full reserves, while Tether processes over $50 billion in daily transactions. These corporate-issued currencies transform how businesses handle international payments.
The Control Factor
Digital currencies operate 24/7 without traditional banking restrictions, which makes them perfect for international business transactions. However, every single transaction gets tracked, recorded, and monitored by the authority that issues them. This level of oversight becomes the defining characteristic that separates digital currencies from their decentralized cousins.
But what happens when you remove that central authority entirely? That’s where cryptocurrency enters the picture.
What Makes Cryptocurrency Different
Cryptocurrency operates without any central authority whatsoever. No government, no bank, no company controls Bitcoin or Ethereum. Instead, thousands of computers worldwide maintain these networks through blockchain technology, where every transaction receives verification from multiple participants before approval. This decentralized structure means no single entity can freeze your account, reverse transactions, or manipulate supply like traditional financial institutions do with digital currencies.
Bitcoin Proves Scarcity Works
Bitcoin caps its total supply at exactly 21 million coins, with over 19.5 million already mined. This mathematical scarcity drives value appreciation over time, unlike government-issued currencies that authorities can print endlessly. Bitcoin has maintained 99.9% uptime since 2009 without a single successful hack of its core network. The network processes roughly 300,000 transactions daily with an average fee of $2-5, which makes it viable for larger transfers but expensive for small purchases.
Ethereum Powers Business Applications
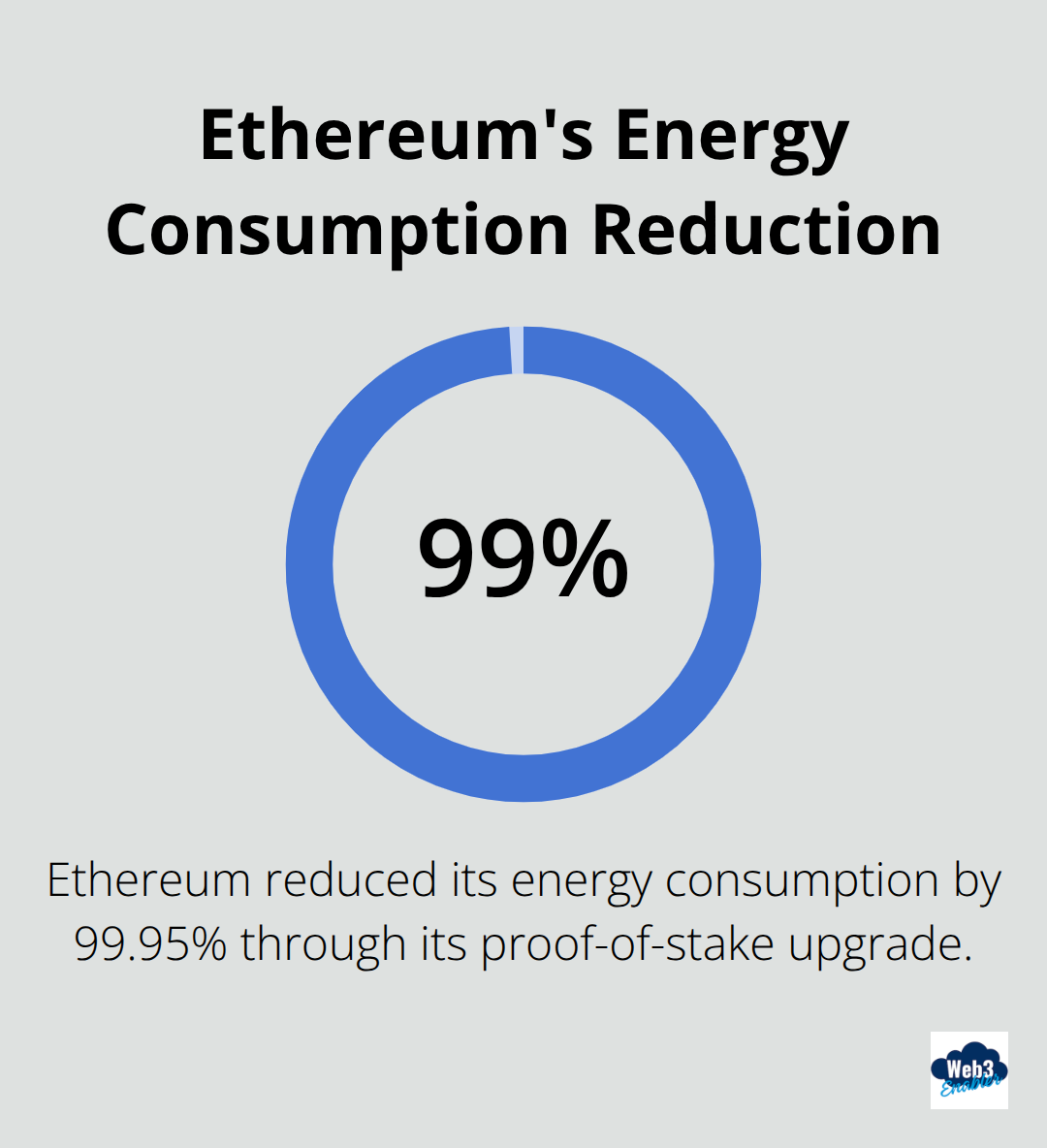
Ethereum extends beyond simple payments by supporting smart contracts and decentralized applications. Major companies like JPMorgan and Microsoft use Ethereum-based systems for supply chain tracking and financial settlements. Ethereum processes over 1 million transactions daily and recently reduced its energy consumption by 99.95% through its proof-of-stake upgrade. Transaction fees fluctuate between $1-20 depending on network congestion, with Layer 2 solutions like Polygon reducing costs to under $0.01 per transaction.
No Permission Required
Cryptocurrencies eliminate traditional gatekeepers entirely. Anyone can send $10 million in Bitcoin globally within 10 minutes for under $5, compared to traditional wire transfers that cost $25-50 and take 3-5 business days. Chainalysis reports that less than 1% of cryptocurrency transactions involve illicit activity (debunking common misconceptions about criminal use). This permissionless nature creates opportunities for businesses to streamline international operations without banking intermediaries.
The fundamental differences between these two digital money types go far deeper than just control structures. The technology, regulations, and business implications create entirely different landscapes for companies to navigate.
Key Differences Between Digital Currency and Cryptocurrency
Digital currencies live under strict government oversight while cryptocurrencies operate as rebellious teenagers who moved out and refuse parental control. The Federal Reserve maintains complete authority over any future digital dollar, with powers to freeze accounts, reverse transactions, and monitor every purchase. China’s digital yuan demonstrates this control perfectly, as central banks can issue CBDCs with expiration dates like coupons and track citizen spending patterns in real-time. The European Central Bank plans similar oversight for its digital euro, with required identity verification for all transactions above 3,000 euros.
Government Control vs Network Consensus
Central banks control digital currencies through direct administrative power. When Nigeria’s central bank wanted to devalue the eNaira, they simply changed numbers in their system overnight. Cryptocurrency networks require consensus from thousands of independent validators before any changes occur. Bitcoin miners spend approximately 150 terawatt-hours annually to secure the network, which makes it virtually impossible for any single entity to manipulate transaction history.
Technology Infrastructure Differences
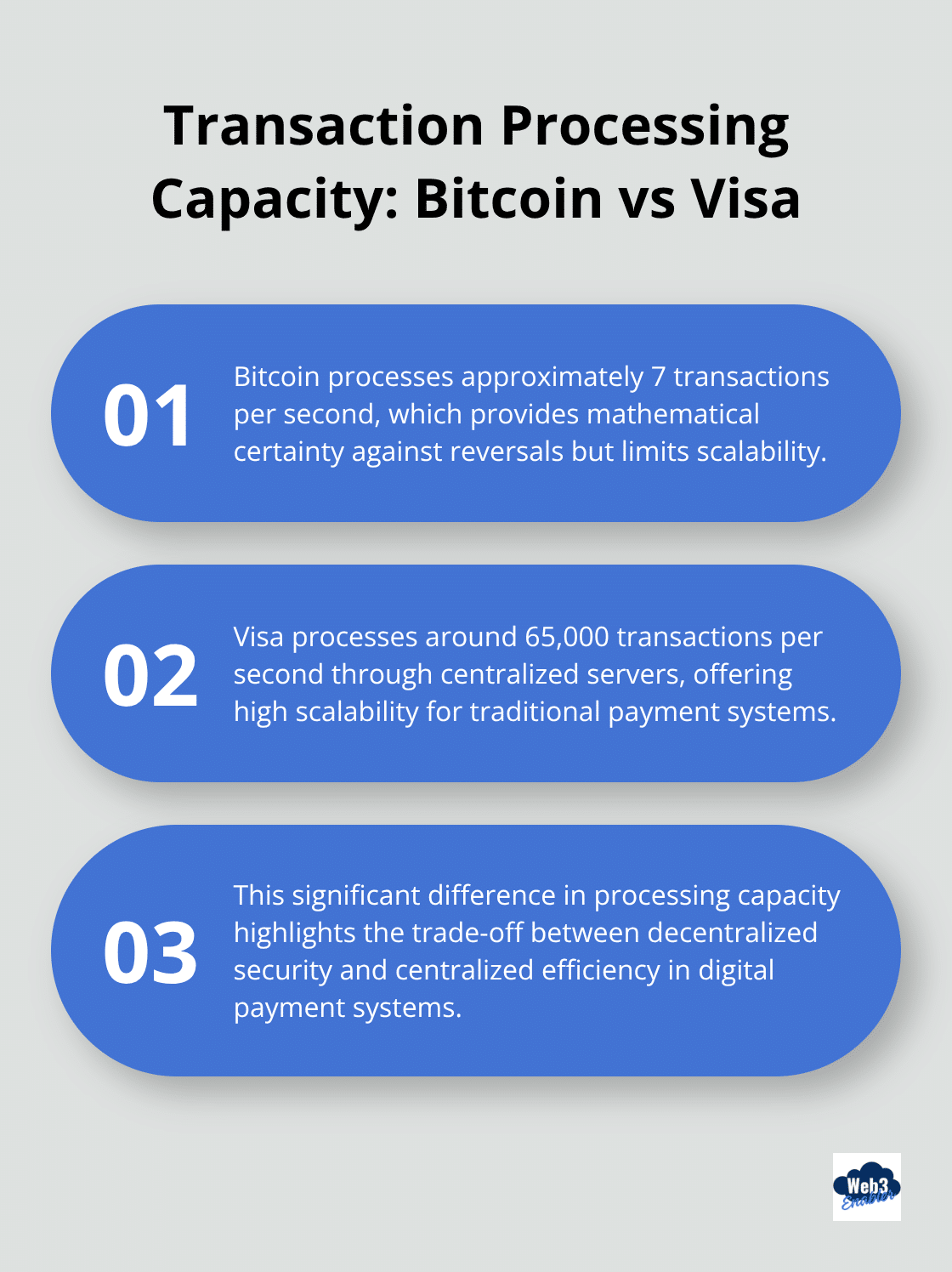
Central bank digital currencies run on centralized databases that governments can update instantly. Traditional banking systems process 65,000 Visa transactions per second through centralized servers, while Bitcoin handles 7 transactions per second but with mathematical certainty that no authority can reverse them. Ethereum’s proof-of-stake system requires validators to stake 32 ETH (roughly $50,000) to participate, which creates financial incentives for honest behavior rather than administrative compliance.
Regulatory Frameworks Shape Operations
The Genius Act now governs payment stablecoins in the United States and requires full reserves and regular audits for companies like Circle. Cryptocurrency exchanges must register with FinCEN and comply with anti-money laundering standards, but the underlying Bitcoin network operates beyond any single jurisdiction’s control. The European Union’s MiCA framework licenses crypto businesses while treating Bitcoin itself as property rather than currency. This creates a fascinating paradox where governments regulate the on-ramps and off-ramps to cryptocurrency but cannot control the highways themselves.
Final Thoughts
The digital currency vs cryptocurrency debate centers on one fundamental question: who controls your money? Digital currencies place governments and corporations in complete control, while cryptocurrencies distribute that power across decentralized networks that nobody owns. This distinction creates vastly different opportunities for modern businesses.
Digital currencies offer regulatory clarity and institutional backing, which makes them ideal for companies that need compliance-friendly payment solutions. Cryptocurrencies provide global accessibility and censorship resistance, appealing to businesses that want financial independence from traditional banks. Financial institutions embrace central bank digital currencies because they maintain existing power structures while adding digital efficiency (yet they must compete with permissionless networks that operate without their involvement).
The future operates on a two-track system where government-issued digital currencies dominate regulated financial services while cryptocurrencies thrive in areas that require decentralization. We at Web3 Enabler help companies navigate this landscape with blockchain solutions that connect traditional business infrastructure with modern payment technologies. The question isn’t whether digital money will replace cash, but which type will power your business operations.







